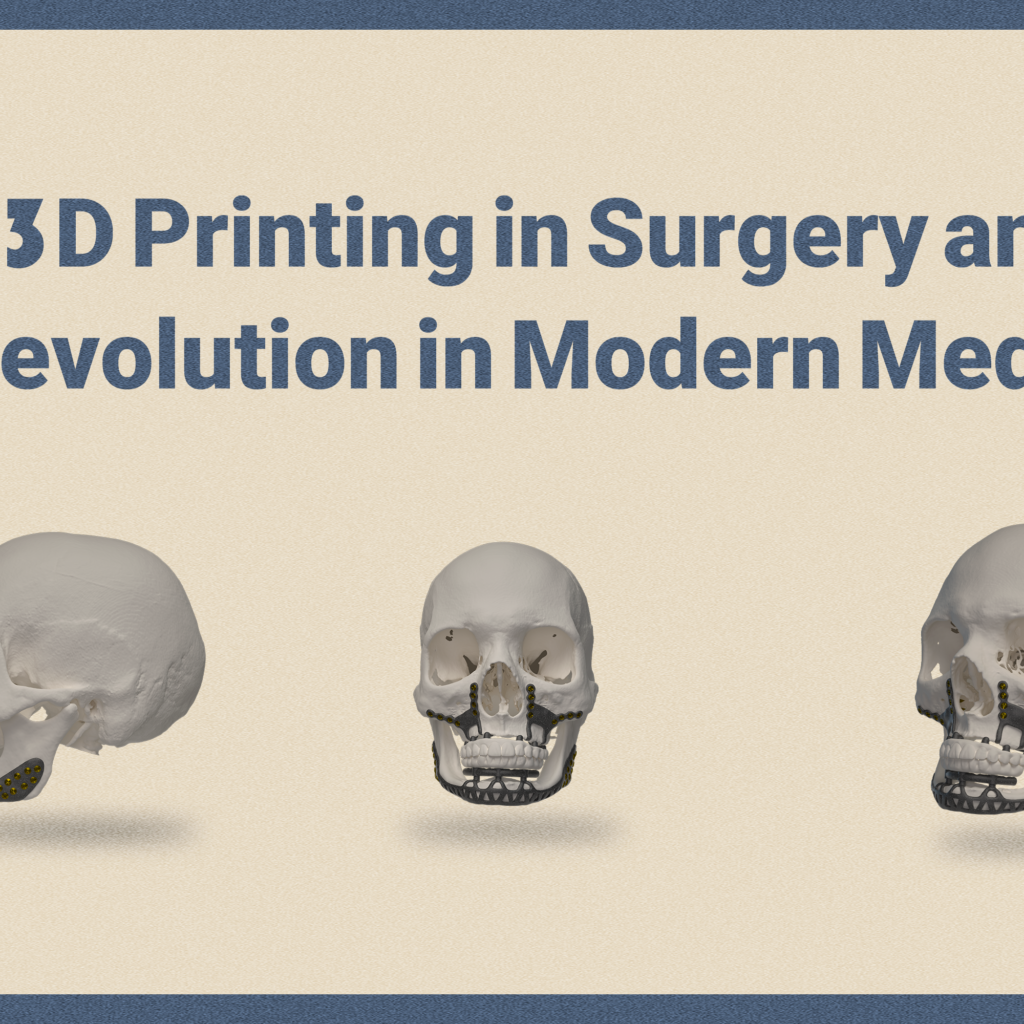
The Benefits and Challenges of Patient-Specific Design

This article want to talk about The Benefits and Challenges of Patient-Specific Design Introduction With the rapid advancement of additive manufacturing and 3D design software, the field of patient-specific design has seen remarkable growth. The global healthcare additive manufacturing market is projected to reach $27.3 billion by 2030, marking a significant transformation in medical […]